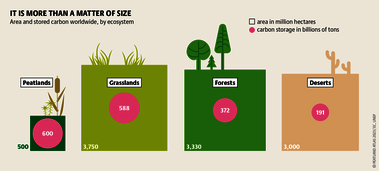
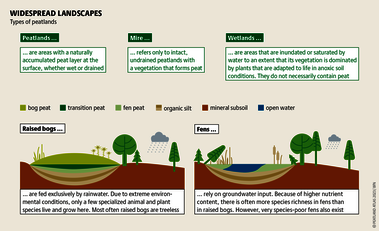
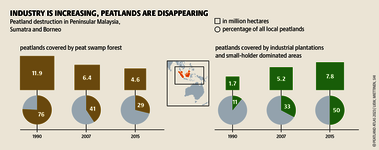
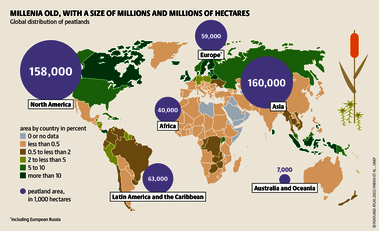
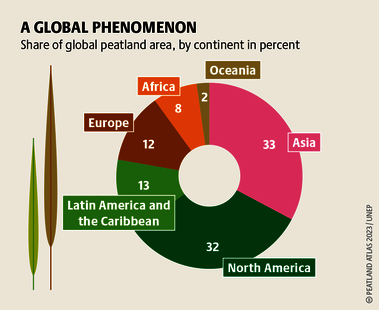
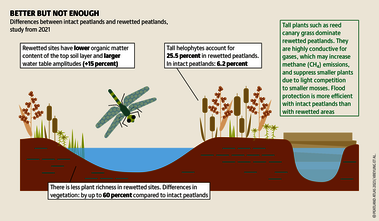
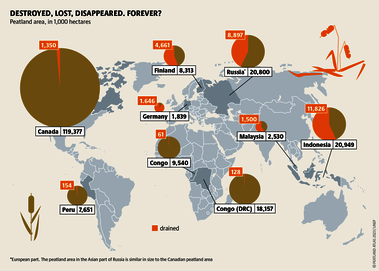
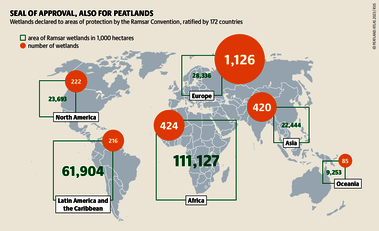
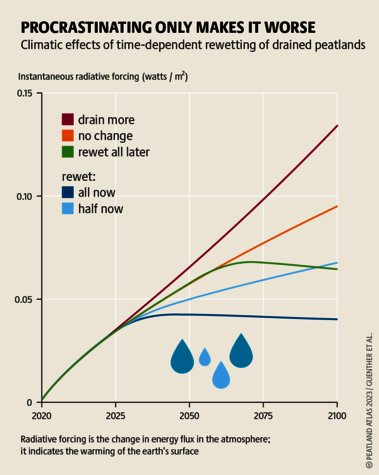
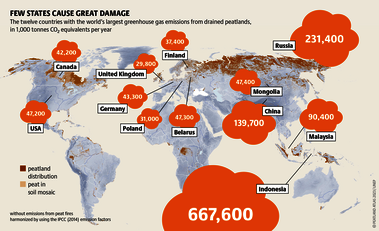
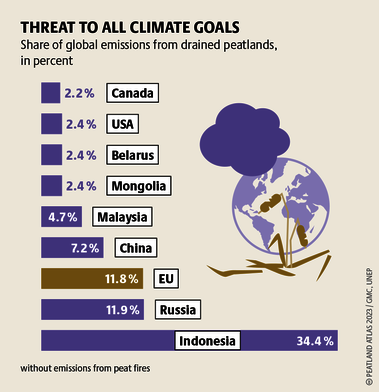
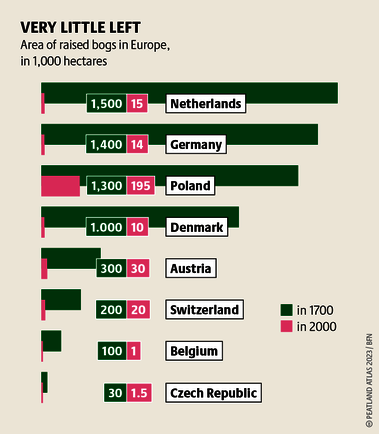
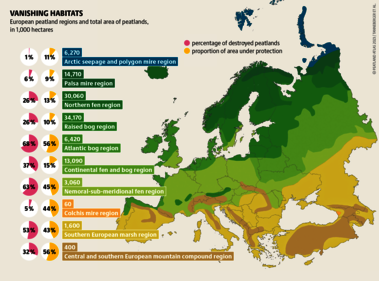
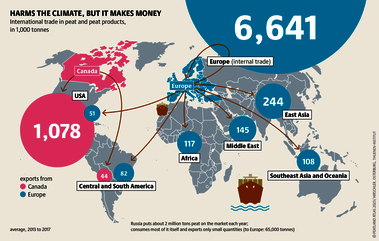
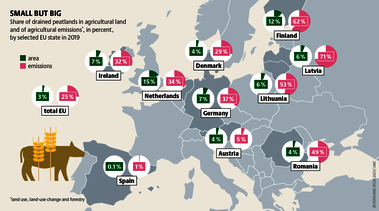
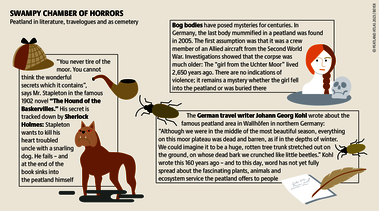
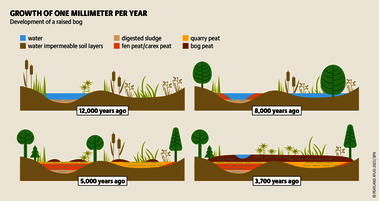
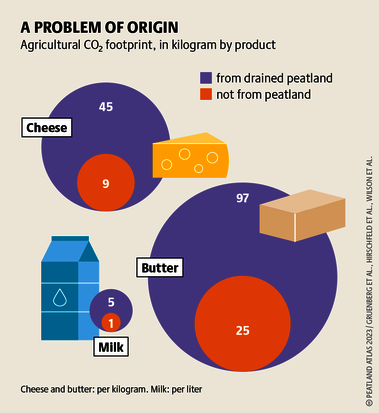
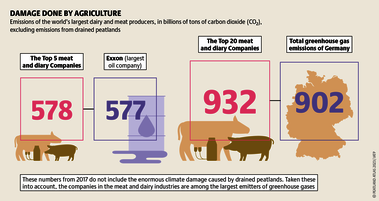
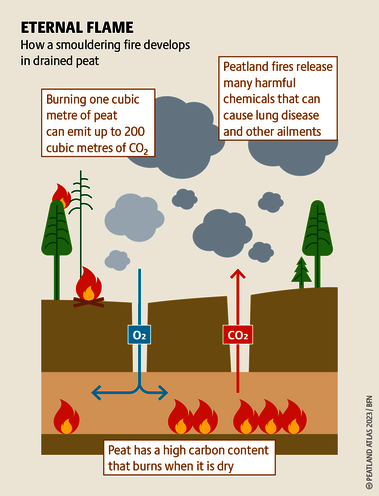
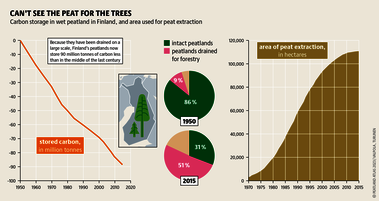
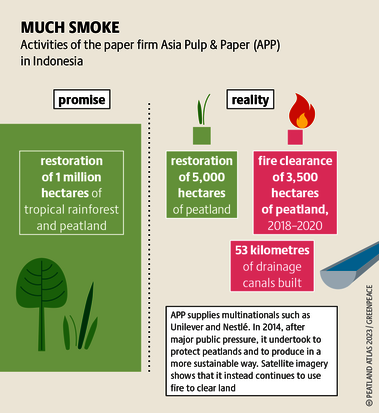
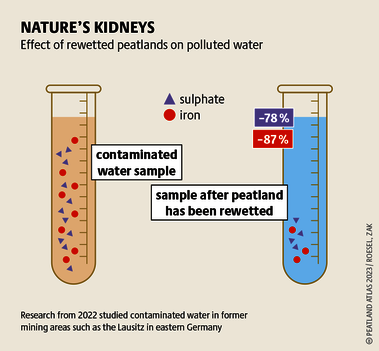
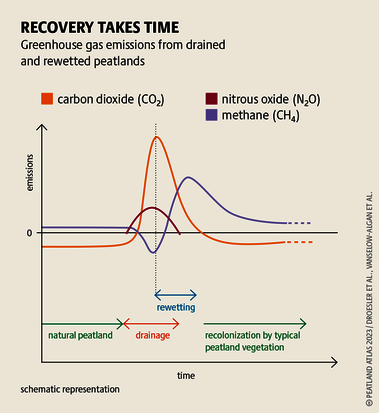
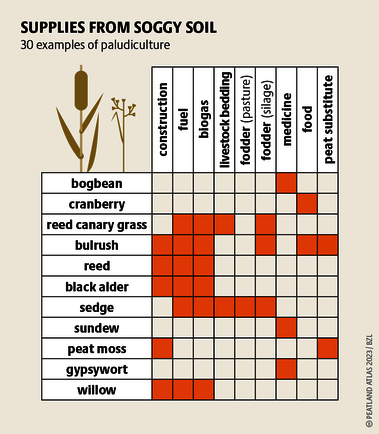
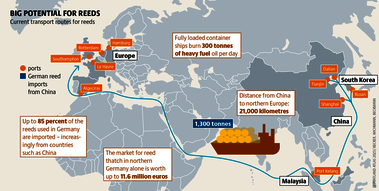
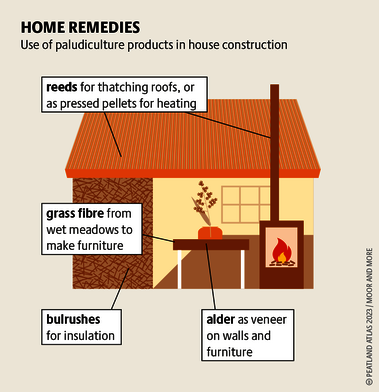
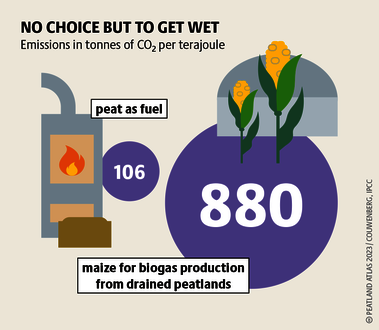
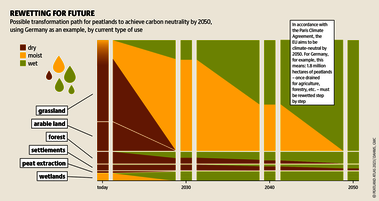
Although peatlands cover only 3% of the world's land, they store about twice as much carbon as in the biomass of all the world's forests combined. Thus, they are incredibly important especially for the climate and biodiversity. But worldwide more than 10 % of the 500 million hectares of peatlands are already drained, in parts of Central Europe well over 90 %. Every year, another 500,000 hectares of peatlands are destroyed. Drainage turns peatlands into climate killers, since - once drained - they release huge amounts of greenhouse gases - from permafrost in the north to palm oil plantations in Indonesia. With more than two billion tonnes of CO2, the draining of peatlands is responsible for about 4% of all human-made emissions globally. In addition, drainage is also disastrous for biodiversity. Unique habitats for specially adapted species are being lost.
This is outlined in the Peatland Atlas 2023 - Facts and figures on wet climate guardians.
It sheds light on the societal perception and history of peatlands, their importance for the global climate and as unique habitats for biodiversity and nature, and their destruction with local and global consequences. It also explains how we can protect peatlands and restore their functionality. It shows the potentials of wet peatlands for climate protection and opportunities for their wet use, called paludiculture, and how decision-makers and society can act now.
The Peatland Atlas is published by the Heinrich-Böll-Stiftung, the Michael Succow Stiftung, partner in the Greifswald Mire Centre, and BUND (Bund für Umwelt und Naturschutz Deutschland/Friends of the Earth Germany), with support of the Global Peatlands Initiative.
Here you may also find the German version, the Mooratlas.

published today by the Heinrich-Böll-Stiftung, the Michael Succow Stiftung (partner in the Greifswald Mire Centre) and BUND with support of the Global Peatlands Initiative
Place: Brussels
Date: 11.09.2023
![[Translate to EN:] Ausschnitt cover Mooratlas Ausschnitt Cover Mooratlas (Bild: Succow Stiftung, Heinrich-Böll-Stiftung, BUND) [Translate to EN:] Ausschnitt cover Mooratlas Ausschnitt Cover Mooratlas (Bild: Succow Stiftung, Heinrich-Böll-Stiftung, BUND)](/fileadmin/_processed_/2/a/csm_Mooratlas_header_dc42ff0e83.png)